Why Should a Cybersecurity Company Care About FTC Guidelines for Cybersecurity Marketing?
Companies face rigorous scrutiny under FTC guidelines for Cybersecurity marketing claims. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has established clear parameters for truthful advertising in this high-stakes domain. Organizations promoting security products or services must navigate complex regulatory requirements, ensuring all assertions remain substantiated by empirical evidence rather than hyperbole. When companies overstate protection capabilities or misrepresent data handling practices, they expose themselves to significant legal liability and enforcement actions. These stringent standards, developed through numerous precedent-setting cases, serve as both protection for consumers and guardrails for marketers in an increasingly vulnerable digital landscape.
Note: This is not meant to be legal advice and is based on our current understanding. For the current and best response, be sure to consult with an attorney.
Key Takeaways
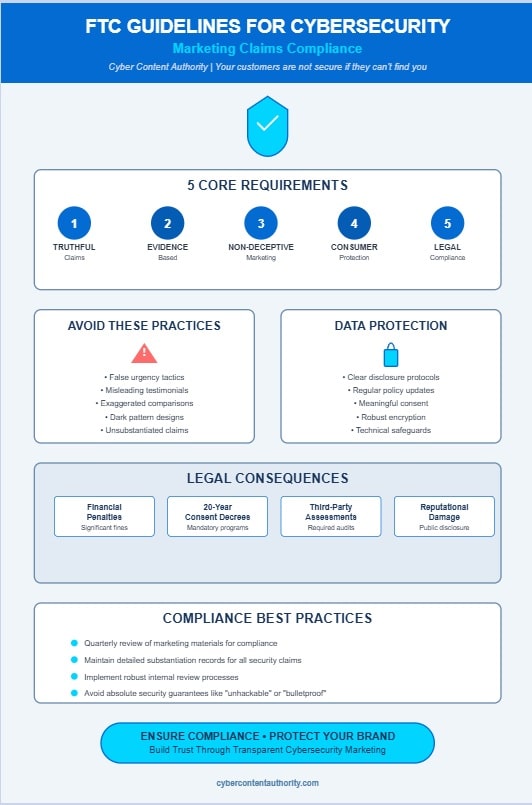
- FTC requires cybersecurity claims to be truthful, evidence-based, and non-deceptive with proportional statements about actual product capabilities.
- Companies must maintain thorough, verifiable technical evidence supporting all security protection assertions and performance metrics.
- Marketing materials must avoid false urgency, misleading testimonials, and exaggerated comparisons that could violate consumer protection standards.
- Clear data handling disclosures are mandatory, including detailed information about personal information collection, storage, and protection methods.
- Violations can result in significant legal consequences including financial penalties, mandatory security program enhancements, and reputational damage.
Truth in Advertising: The FTC’s Core Requirements

While many cybersecurity companies aggressively market their products and services in today’s threat-laden digital landscape, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) maintains stringent guidelines governing all advertising claims, particularly those related to security capabilities.
At the foundation of these regulations, which form the cornerstone of advertising ethics, are five essential requirements: truthfulness in all claims, evidence-based assertions, non-deceptive marketing practices, robust consumer protection mechanisms, and thorough compliance with relevant laws. Small businesses must recognize that implementing these marketing guidelines helps establish proper security culture throughout their organization.
Companies that adhere to these principles not only avoid potentially devastating penalties but also cultivate sustainable consumer trust—a particularly valuable commodity in the cybersecurity sector, where credibility directly impacts purchase decisions.
Substantiating Security Claims With Evidence
Because regulatory expectations for cybersecurity marketing have intensified in recent years, companies must now provide thorough, verifiable evidence to support any assertions about their products’ protection capabilities or effectiveness.
Today’s cybersecurity marketing demands rock-solid evidence behind every protection claim, as regulators increasingly scrutinize product effectiveness assertions.
The FTC’s evidence requirements necessitate extensive technical data, independent testing results, and continuous monitoring documentation to validate marketing claims.
When establishing claim verification protocols, organizations should maintain detailed substantiation records that demonstrate a reasonable basis for each security assertion, particularly since material claims directly influence consumer purchasing decisions.
Furthermore, businesses that leverage competitor comparisons or technical specifications must guarantee these statements withstand regulatory scrutiny through independent verification mechanisms, consequently avoiding potential consequences including regulatory enforcement actions, reputational damage, and market share erosion. According to FTC standards, companies must have adequate evidence before making any cybersecurity claims in their advertising materials.
Common Misleading Marketing Practices to Avoid
The substantiation of security claims represents only one component of FTC compliance; equally important is the avoidance of misleading marketing practices that can trigger regulatory scrutiny and undermine consumer trust.
Organizations must vigilantly avoid creating a false urgency through manufactured threats, which manipulates consumers into making hasty purchasing decisions without adequate consideration of actual security needs.
Furthermore, the utilization of misleading testimonials, particularly those from unqualified sources or fabricated entities, constitutes a significant violation of FTC guidelines.
These deceptive endorsements deliberately misrepresent product efficacy and reliability, thereby preventing consumers from making informed decisions based on legitimate performance data.
This is especially relevant for small business owners considering that more than 70% of cyber attacks target small businesses, making them particularly vulnerable to deceptive cybersecurity marketing.
Guidelines for Data Protection Statements

Effective data protection statements serve as foundational documents for establishing consumer trust and regulatory compliance, requiring organizations to carefully balance transparency, accuracy, and completeness in their communications about data handling practices.
When developing these critical statements, companies must adhere to specific FTC guidelines that emphasize clarity and consumer empowerment, particularly regarding data collection and security practices.
- Implement extensive disclosure protocols that explicitly articulate all aspects of personal information collection, storage, and transmission methodologies.
- Maintain regular policy updates that reflect evolving security practices and regulatory requirements.
- Incorporate clear consent mechanisms that provide consumers with meaningful choice regarding their data.
- Establish robust encryption and technical safeguards that protect sensitive information throughout its lifecycle.
Companies should avoid deceptive “dark patterns” that could manipulate users into sharing more information than they intend to, as the FTC specifically cautions against dark patterns in human-centric security design.
Case Studies: FTC Enforcement Actions on Deceptive Claims
Landmark decisions throughout the Federal Trade Commission‘s enforcement history demonstrate the agency’s commitment to holding companies accountable for misleading cybersecurity claims, establishing precedents that shape industry practices and compliance standards.
The Wyndham Worldwide case analysis serves as a pivotal example wherein the corporation’s failure to implement reasonable security measures, despite promises in their privacy policy, resulted in substantial consumer data breaches, thereby confirming the FTC’s authority to regulate cybersecurity practices.
The enforcement impact extends beyond individual cases, as the more than 50 data security enforcement actions have collectively established that companies making unsubstantiated security claims will face regulatory consequences, typically resulting in twenty-year consent decrees requiring thorough security program implementation. These consent decrees have evolved significantly over time, with recent actions incorporating more specific language following the influential 2019 LabMD case ruling by the Eleventh Circuit.
Best Practices for Adhering to FTC Guidelines for Cybersecurity Marketing Claims
Companies marketing cybersecurity products must substantiate their claims beyond mere feature lists, considering how reasonable consumers might interpret those claims in light of the current threat landscape.
When making security assertions, organizations should exercise caution to avoid overstatements about protection capabilities, especially those suggesting foolproof or absolute protection against all possible threats.
According to FTC enforcement patterns, claims must be proportionate to actual product capabilities, with detailed technical specifications and independent testing documentation readily available to support marketing statements throughout the product lifecycle.
Substantiate Beyond Features
Cybersecurity vendors must transcend mere feature enumeration when marketing their products, as the FTC’s substantiation requirements demand evidence that extends well beyond technical specifications or capability lists.
When developing marketing materials, companies should incorporate empirical validation through performance metrics that demonstrate real-world effectiveness, rather than relying solely on theoretical capabilities.
- Independent third-party testing results that verify security claims
- Quantifiable performance metrics from actual deployments
- Verified user testimonials documenting measurable security improvements
- Transparency reports detailing threat detection and response capabilities
Moreover, substantiation should encompass documentation of how security features function within integrated environments, considering that cybersecurity solutions rarely operate in isolation from other systems. Companies must ensure all cybersecurity claims have sufficient reasonable basis according to the FTC’s Pfizer factors, which assess the type of product, claim, and benefit to consumers.
Avoid Security Overstatements
While substantiating claims with robust evidence forms a cornerstone of compliant cybersecurity marketing, vigilantly avoiding security overstatements represents an equally important dimension of FTC compliance.
Companies must implement extensive compliance strategies, which necessitate careful language review, particularly regarding absolute security guarantees that may trigger regulatory scrutiny.
The overstatement risks extend beyond mere FTC enforcement actions, as businesses face potential reputation damage and consumer trust erosion when security claims prove exaggerated.
When crafting marketing materials, organizations should consistently assess whether claims such as “unhackable,” “bulletproof,” or “impenetrable” can be objectively demonstrated through rigorous testing and real-world performance data.
Legal Consequences of Overstating Security Capabilities
Exaggerating cybersecurity capabilities in marketing materials represents a serious legal liability that extends far beyond mere promotional hyperbole, as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) actively monitors and enforces against such deceptive practices under its broad consumer protection mandate.
Organizations misrepresenting cybersecurity capabilities face severe consequences that undermine market credibility and stakeholder confidence.
Organizations found in violation face substantive repercussions, which erode consumer trust and damage market positioning.
Consequences typically include:
- Binding consent decrees mandating extensive security program implementation
- Mandatory third-party security assessments for up to 20 years
- Significant financial penalties for non-compliance with FTC orders
- Public disclosure of violations, resulting in reputational damage
Balancing Effective Marketing With Regulatory Compliance

Marketing professionals operating within the cybersecurity sphere must navigate the complex intersection of promotional efficacy and FTC compliance, especially regarding truth in advertising principles that prohibit deceptive or misleading representations about product capabilities.
Organizations seeking to promote their cybersecurity offerings effectively, without triggering regulatory scrutiny, should implement rigorous internal review processes that verify all claims against documented evidence, including technical specifications, testing results, and independent assessments.
The substantiation of security claims requires not only technical accuracy but also contextual appropriateness, ensuring that marketing materials convey realistic expectations about protection levels, threat mitigation capabilities, and potential limitations of cybersecurity products or services in varying implementation scenarios.
Truth In Advertising
Since companies must navigate the complex intersection between promoting their cybersecurity capabilities and adhering to stringent regulatory requirements, truth in advertising has emerged as a cornerstone principle in cybersecurity marketing practices.
The FTC, through its rigorous enforcement of truthful advertising and ethical marketing standards, expects organizations to substantiate all security-related claims with verifiable evidence, considering misleading statements potentially deceptive and actionable.
Key requirements include:
- Maintaining alignment between advertised capabilities and actual security implementations
- Avoiding exaggerated or unsubstantiated claims about cybersecurity effectiveness
- Providing clear, supportive evidence for all security assertions
- Regularly reviewing marketing materials against evolving security practices
Substantiating Security Claims
Every cybersecurity vendor must definitively substantiate their security claims with compelling, verifiable evidence that satisfies increasingly stringent FTC requirements, while simultaneously crafting marketing messages that resonate with potential customers.
Within the evidence hierarchy, scientific studies and independent verification methods rank highest, followed by user data and internal testing protocols. Companies failing to adequately support their assertions face significant legal repercussions, including FTC enforcement actions that may result in substantial financial penalties and irreparable reputational damage.
In addition, documentation transparency remains critical, as all testing methodologies, technical specifications, and performance limitations must be readily accessible through a systematically organized verification framework that withstands regulatory scrutiny.
Look Into FTC Guidelines for Cybersecurity Marketing Claims So You’re Compliant!
Adherence to FTC guidelines for cybersecurity marketing claims, which necessitate truthfulness, substantiation, and transparent communication, remains essential for organizations seeking to maintain regulatory compliance while building consumer trust. Companies that implement robust verification processes for security claims, avoid deceptive practices, and accurately represent data protection capabilities not only mitigate legal liability but also distinguish themselves as credible market participants in an increasingly security-conscious digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Often Should Cybersecurity Marketing Materials Be Reviewed for Compliance?
Organizations should conduct regular audits of cybersecurity marketing materials quarterly, while implementing compliance checklists to guarantee alignment with evolving regulations and prevent misleading claims that could trigger enforcement actions.
Can Competitor Comparisons Be Made in Cybersecurity Marketing Claims?
Companies can make truthful competitor comparisons in cybersecurity marketing. Effective comparison strategies highlight verifiable advantages while avoiding misleading competitor claims that could trigger FTC enforcement actions.
Do FTC Guidelines Apply to B2B Cybersecurity Marketing?
FTC guidelines apply to B2B cybersecurity marketing, governing truthful B2B claims and enforcing cybersecurity ethics. Companies must substantiate performance capabilities and competitive advantages regardless of their business customer audience.
Are Social Media Posts Subject to the Same FTC Scrutiny?
Social media posts are equally subject to FTC scrutiny. Digital marketing ethics demand social media compliance regardless of platform, with companies being held accountable for misleading claims made through any online channel.
How Do International Cybersecurity Standards Impact FTC Compliance Requirements?
International standards complement FTC compliance requirements, creating a cybersecurity framework that transcends borders. Organizations leveraging global benchmarks often exceed domestic thresholds while traversing the complex regulatory landscape with greater agility.

